
According to a new report from the IoT analyst firm Berg Insight, the installed base of smart gas meters in Europe amounted to 45.9 million units in 2021, equal to a penetration rate of 38 percent.
The installed base will continue to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7 percent between 2021 and 2027, reaching 75.9 million units at the end of the period. Annual shipment volumes amounted to 6.6 million in 2021 and are expected to gradually decrease in the coming years with the completion of several large-scale nationwide rollouts. France, the UK, Italy and the Netherlands were the most active markets in 2021, together accounting for close to 95 percent of all smart gas meter shipments during the year. While the rollouts in Italy, France and the Netherlands will soon be completed, the UK market is on the other hand after several delays expected to ramp up yearly installations to reach a high of 3.4–3.6 million units per year during 2023–2025. Belgium and Ireland are two other markets that are expected to contribute with significant shipment volumes in the next few years.
The smart gas meters deployed in Europe have over the past years not been networked in quite the same way as their counterparts in the electricity sector. A common model, observed for example in the UK, the Netherlands and Belgium, is to utilize a local wireless or wired interface to transmit gas data via the customer’s smart electricity meter. A mix of 169 MHz RF and 2G/3G cellular communications has meanwhile been the primary model for the largest projects in which smart gas meters have been deployed independently of smart electricity meters, such as in Italy and France. A change of the status quo might now however be on the horizon as new types of LPWA technologies have become more readily available in the past couple of years.
Mattias Carlsson, IoT Analyst at Berg Insight, said:
“The Italian gas sector became the first in Europe to initiate large-scale adoption of NB-IoT as a primary smart meter connectivity choice and in 2021 the installed base of gas meters with NB-IoT connectivity almost doubled in the country to reach 1.7 million at the end of the year.”
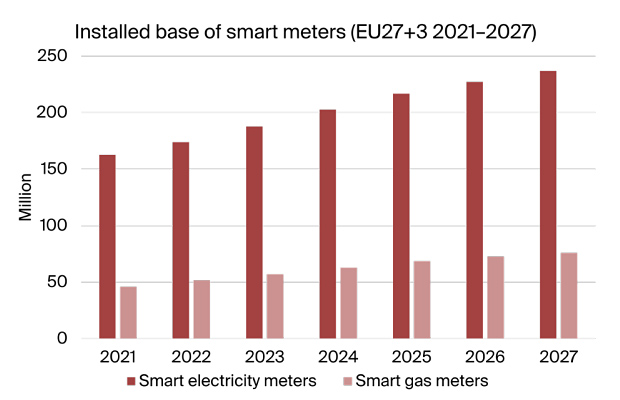
The composition of communication technology in the installed base of smart gas meters is thus expected to shift in the coming years. In 2021, 169 MHz RF was the most common communications technology with a market share of 40 percent. By 2027, Zigbee is expected to surpass 169 MHz RF to become the most prevalent connectivity option with an installed base of close to 24.9 million units. NB-IoT/LTE-M is moreover expected to grow with an impressive CAGR of 35.6 percent during 2022–2027 to reach an installed base of 10.7 million units in 2027, making it the third most common connectivity option on the European smart gas meter market.
Another emerging technology trend is the anticipated increase in the use of hydrogen in European gas supply operations. “As the properties of hydrogen differ significantly from those of natural gas, meter vendors will have to put in place relevant technological and strategic roadmaps in order to position themselves in the new European renewable energy sector”, concluded Mr. Carlsson.







